Third-party risk management (TPRM) definition
Working with a third party can introduce risk to your business. If they have access to sensitive data they could be a security risk, if they provide an essential component or service for your business they could introduce operational risk, and so on. Third party risk management enables organizations to monitor and assess the risk posed by third parties to identify where it exceeds the threshold set by the business. This allows organizations to make risk-informed decisions and reduce the risk posed by vendors to an acceptable level.
TPRM is the process of detecting and addressing any form of risk linked with third-party entities (for example, financial, fraud, or cyber risk). A third party is an entity that directly offers a product or service to your consumers and/or an entity that is vital to your everyday operations.
Why is third-party risk management important?
Third parties are an important key to the success of a business. Organizations of all sizes are becoming more and more reliant on third parties for their innovation, growth, and digital transformation.
But, a strong reliance on third parties can be risky. The risk posture of a third party is crucial to the risk posture, resilience, and reputation of a company using a third party. It can be very costly and difficult to deal with a third party incident, with consequences including regulatory actions, damage to reputation, and a loss of revenue. Third parties need to be carefully vetted with ongoing risk assessments to ensure that an organization is protected and secure.
What we do:
RNR’s third-party vendor management system (TPRM) is a software application that helps organizations manage their relationships with third-party vendors. RNR’s TPRM system can help organizations to:
- Identify and assess risks associated with third-party vendors: Our TPRM system can help organizations to identify and assess the risks associated with their third-party vendors. This includes identifying the vendors that have access to sensitive data, the risks associated with those vendors, and the steps that can be taken to mitigate those risks.
- Select and onboard third-party vendors: Our TPRM system can help organizations to select and onboard third-party vendors. This includes evaluating vendors, negotiating contracts, and ensuring that vendors meet the organization’s security requirements.
- Monitor and manage third-party vendors: Our TPRM system can help organizations to monitor and manage their third-party vendors. This includes conducting audits, reviewing vendor reports, and taking corrective action when necessary.
- Terminate relationships with third-party vendors: Our TPRM system can help organizations to terminate relationships with third-party vendors in a smooth and orderly manner. This includes ensuring that all data is returned to the organization and that all contracts are terminated properly.
TPRM systems can be a valuable tool for organizations that want to improve their third-party risk management. By using our TPRM services, organizations can reduce their risk of data breaches and other security incidents. Get in touch now and secure your business and strengthen relationship with your vendors.

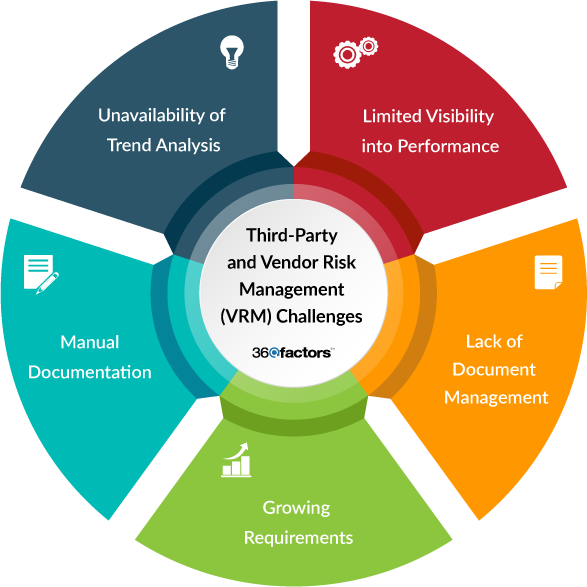
Risk management challenges
Prior to now, vendor risk management has been time-consuming and error-prone, consisting of manual processes using emails, spreadsheets, and siloed vendor risk management tools. These processes and tools are simply inadequate —neither the tools nor the teams can keep up with the growing number of third parties. Common challenges faced by enterprises who haven’t implemented modern or comprehensive solutions include:
- Manual Processes: Low efficiency with monitoring third parties and a longer amount of time to find and mitigate issues.
- Lack of scalability: Teams cannot keep pace with third party management when they are using a tool that will not scale, which can increase risk.
- Siloes: Too many siloes can create difficulty accessing risk information across the organization.
- Disconnected: No enterprise context makes it difficult to prioritize third party risks through the vendor lifecycle or when requirements change.

Considerations for onboarding a vendor
Below are some important considerations that need to be taken into account when choosing a third party. The answers will determine the level of risk they pose to the business:
- What type of data is being accessed? What type of access has been granted?
- Do they work with 4th parties that could pose delivery challenges?
- Are they in an unstable part of the world?
- Are they providing a critical product or service? If so, do we need to have an alternate vendor in place? ?
- What is their security history, what best practices do they have in place and execute on? (basic hygiene, patching SLAs, history of breaches, etc.)
- Do they have business continuity plans in place?
- Are they in compliance with the regulations your organization has identified?
- What is their financial situation?
The areas of risk
01
Strategic risk


02
Reputation risk
03
Operational risk


04
Transaction risk
05
Compliance risk


06
Information security risk
07
Financial risk

Leave us message

