Resource as Service (for Pen-testing and GRC)
Resource as a Service (RaaS) is a delivery model in which organizations can purchase security testing and compliance services on demand. RNR offers a variety of services, including penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and compliance assessments.
RNR’s RaaS can be a cost-effective way for organizations to get the security testing and compliance services they need. RNR has a large pool of security experts who can be quickly deployed to conduct testing and assessments. This can be helpful for organizations that need to conduct security testing or compliance assessments on a tight deadline.
RNA’s RaaS is a scalable way for organizations to get the security testing and compliance services they need. RNR can scale services to meet the needs of organizations of all sizes. This can be helpful for organizations that need to conduct security testing or compliance assessments on a regular basis.
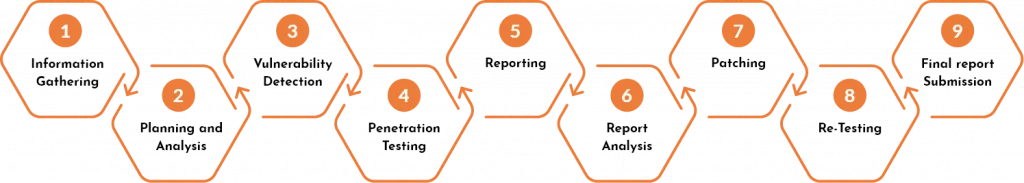
Web Application Penetration Testing Methodology
With years of experience across application threat surfaces such as online, mobile, and cloud, RNR provides on-premises and off-premises application security services with the below roadmap:
We Comply with all the Top IT Security Testing Guidelines
What we do:
As a RaaS provider we give the following:
- Experience: RNR has wide experience in the industry and with the specific regulations that apply to your organization.
- Skills: RNR has the skills and expertise to conduct the security testing and compliance assessments that you need.
- Availability: RNR is available to meet your needs and to provide the level of support that your business require.
- Cost: RNR is affordable yet par excellence in services.
If you are looking for a cost-effective, scalable, and convenient way to get the pen-testing and GRC services you need, then RNR’s is right here for you.

Industry ‘s Best Security Standards
Our team of Professional Experts employs best-in-Industry security standards including
OWASP Secure Coding Guidelines
The Open Web Application Security Project is an online community dedicated to the creation of free, open-source publications, documentation, tools, and technologies in the field of Web application security.
OWASP Secure Coding Checklist are
- Input Validation
- Access Control
- File Management
- Memory Management
- Cryptographic Practices
- Communication Security
- General Coding Practices
- Output Coding
- File Management
- Database Security
- Session Management
- Error Handling and Logging
- System Configuration
- Authentication and Password Management

SANS25 Secure Coding Guidelines
A well-known compilation of the most frequent security vulnerabilities found in all types of systems, with the goal of installing security into every developer’s head.
- Out-of- Bounds read and Write
- Improper Authentication
- Unrestricted Upload of File with Dangerous Type
- Null Pointer Dereference
- Improper Control of Generation of Code
- Improper Certificate Validation
High Level Test Cases
Black Box Assessment
- Cryptography
- Configuration Testing
- Deploy Management Testing
- Information Gathering
- Data Validation Testing
Grey Box Assessment
- Identify Management Testing
- Authorization Testing
- Input Validation Testing
- Authentication Testing
- Session Management Testing
- Business Logic Testing
Security Testing Methodology
01
RECONNAISSANCE
One of the most important tasks in an application pen test is reconnaissance, often known as information gathering. In a web application penetration test, the initial phase is all about gathering as much information as possible about the target application. Few examples of testing: Conduct Search Engine Reconnaissance and Discovery for Information Leakage, Search Engine Recon, App Enumeration, and App Fingerprinting Determine the app’s entrance point.


02
CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT
Understanding the deployed configuration of the server/infrastructure that hosts the web application is almost as important as performing application security testing. Although application platforms are diverse, several fundamental platform configuration issues, like how an unsecured program can compromise the server (insecure HTTP methods, old/backup files), can endanger the application. Few examples are – TLS Security, App Platform Configuration, File Extension Handling, and Cross Site Tracing. HTTP tight transport security, HTTP methods, and file permissions are all tested.
03
AUTHENTICATION TESTING
The process of attempting to validate the digital identity of a communication’s sender is known as authentication. The log on process is the most common example of such a procedure. Understanding how the authentication process works and using that knowledge to defeat the authentication mechanism is what testing the authentication schema entails. Few examples are – Poor lockout mechanism, bypassing authentication schema, browser cache weakness, and weak authentication in alternative channel.


04
SESSION MANAGEMENT
05
AUTHORIZATION TESTING
Authorization is a step that follows successful authentication; therefore, the pen tester will confirm this after confirming that he or she has legitimate credentials that are associated with a well-defined set of roles and privileges. Few Examples are Directory traversal, privilege escalation and bypassing authorization controls, and insecure direct object reference. Understanding how the authorization process works and exploiting that knowledge to go around the authorization system is what authorization testing entails.


06
DATA INPUT VALIDATION

07
TESTING FOR ERROR HANDLING
During a web application penetration test, we frequently run into a slew of error codes emitted by apps or web servers. It’s possible to display these problems by utilizing a specific request, either built manually or with the help of tools. These codes are extremely beneficial to penetration testers since they expose a wealth of information about databases, flaws, and other technological components that are directly tied to web applications. Few examples are -Analyzing Error Codes and Analyzing Stack Traces.
08
TESTING FOR BUSINESS LOGIC


09
CLIENT- SIDE TESTING
Client-side testing is concerned with the execution of code on the client, which is usually done natively within a web browser or a browser plugin. The execution of code on the client side differs from the execution of code on the server and the subsequent return of content. Few Examples are – JavaScript execution, client-side URL redirection, cross-origin resource sharing, and manipulation.
10
DENIAL OF SERVICE (OPTIONAL)
A denial of service (DoS) attack aims to prevent legitimate users from accessing a resource. Denial of service (DoS) attacks have traditionally been network-based, in which a malicious user floods a target system with enough traffic to render it unable to serve its intended users. This phase of. testing will concentrate on application layer attacks on availability that can be carried out by a single rogue user on a single system.


11
REPORTING
The goal of the reporting step is to deliver, rank, and prioritize findings, as well as to provide a clear and actionable report with supporting evidence for project stakeholders. This is the most critical phase for us at Kratikal, and we take great care to make sure we’ve clearly explained the value of our service and discoveries.
Tools Used
We use industry benchmark security testing tools across each of the IT infrastructure as per the business and technical requirements.
Below are few from many of the tools we use:
Burpsuite
Nessus
Nmap
Acunetix
Net Sparker
DIRB
Trusted by International Brand





























What is Application Security?
Effective Security Testing Safeguards your Applications from Cyber Threats & Vulnerabilities
RNR Application Security Testing helps you detect application vulnerabilities, provide full coverage for Web and Mobile application infrastructure and online services, and reduce risks to meet regulatory compliance requirements. Our Application Security Methodology extends beyond scanning software detection to identify and prioritize the most vulnerable aspects of your online application, as well as come up with practical Solutions.
Leave us message









